Living with constant hip pain can affect everything—from walking and sleeping to enjoying daily life. When mobility starts declining and discomfort doesn’t go away with rest or medication, it may signal a more serious issue. “10 Warning Hip Replacement Symptoms You Must Know: Costs & Global Comparison” serves as your comprehensive guide to recognizing when hip pain becomes a sign of joint deterioration rather than temporary strain.

From stiffness and swelling to pain that radiates through the thigh or groin, identifying the right symptoms early can make all the difference. This in-depth article not only uncovers critical hip replacement symptoms but also compares treatment costs and quality of care across the U.S., Türkiye, and India—helping patients make informed and confident decisions.
Table of Contents
10 Warning Hip Replacement Symptoms
Hip pain that lingers, limits movement, or disrupts sleep often signals a deeper problem. When stiffness, swelling, or pain in the groin or thigh becomes constant, it may be time to consider a hip replacement. Recognizing these early warning signs helps prevent further damage and supports better long-term mobility. Understanding when to take action can make a major difference in comfort and quality of life.
This guide explains the key symptoms that may point to hip replacement, including dislocation, infection, and post-surgery issues like hip flexor tendonitis or trochanteric bursitis. It also explores how doctors confirm the need for surgery using X-rays and MRIs, and how to tell if the pain is from arthritis or bursitis instead.
Beyond symptoms, cost plays a major role in treatment decisions. Comparing hip replacement expenses in the US, Türkiye, and India reveals where patients can find both affordability and reliable care. By the end, anyone facing hip pain will understand how to identify the warning signs, confirm the diagnosis, and choose the best treatment option for their needs.
When hip pain and stiffness begin to affect mobility, daily activities, and rest, it may signal serious joint damage. Recognizing these signs early helps people seek medical advice before the condition worsens, improving treatment outcomes and preserving joint function.
Persistent Hip Pain and Stiffness
Constant pain in the hip joint often indicates cartilage wear or arthritis. The discomfort may start as mild soreness but can progress into sharp or aching pain during movement or rest.
People often notice stiffness after sitting for long periods or upon waking up. This stiffness makes it harder to bend, rotate, or move the leg freely. When pain continues despite medication or physical therapy, doctors may consider imaging tests to check for joint deterioration.

Persistent pain also affects posture and gait. Over time, the body compensates by shifting weight to the other leg, which can lead to additional strain and imbalance.
Difficulty Walking or Standing
Hip joint damage often causes difficulty walking or standing for long periods. The joint may feel weak or unstable, making each step painful.
People may limp or take shorter strides to avoid discomfort. Climbing stairs or standing from a seated position becomes challenging, especially when the hip joint loses flexibility.

Doctors often assess walking patterns and balance to evaluate hip function. Persistent difficulty walking or standing may suggest advanced joint degeneration, which can limit independence and mobility.
Limited Range of Motion
A reduced ability to move the hip smoothly or fully is a key warning sign. Tasks like tying shoes, crossing legs, or getting into a car may become difficult.
Limited range of motion often results from inflammation, cartilage loss, or bone spurs. The joint may feel tight or “locked” during certain movements.

Physical tests help measure how far the hip can move in different directions. When range of motion continues to decline, it can signal that non-surgical treatments are no longer effective.
Hip Joint Crepitus or Grinding
Crepitus refers to a grinding, clicking, or popping sound in the hip joint during movement. It occurs when rough bone surfaces rub together due to cartilage loss.
This sensation often comes with pain or stiffness. Over time, the grinding may become more noticeable and frequent.
Doctors may use imaging tests to confirm whether the noise is from joint degeneration or another cause. Persistent crepitus combined with pain often indicates advanced arthritis or joint wear that may require surgical evaluation.
Loss of Quality of Life
Severe hip pain and stiffness can limit independence and reduce overall quality of life. Simple activities—like walking, dressing, or shopping—can become exhausting.
Chronic discomfort may lead to frustration, reduced social interaction, and decreased physical activity. People often avoid movement to prevent pain, which can weaken muscles and worsen mobility issues.

When hip problems start to interfere with hobbies, work, or relationships, it becomes important to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider.
Reliance on Mobility Aids
Using a cane, walker, or crutch to move around often signals significant joint deterioration. These aids help reduce pressure on the hip but also show that the joint can no longer support normal activity.
People may start depending on railings or furniture for balance. This reliance can cause uneven weight distribution, leading to muscle strain and fatigue.

If mobility aids become necessary for basic movement, doctors may recommend evaluating whether a hip replacement could restore stability and function.
Chronic Night or Rest Pain
Pain that continues during rest or sleep suggests advanced joint damage. The hip may ache even when lying still, making it difficult to find a comfortable position.
Inflammation and bone friction often cause this type of pain. It can disrupt sleep and lead to fatigue, which further reduces energy and mood.

Chronic night pain is a strong indicator that conservative treatments are no longer effective, and imaging may be needed to assess the extent of joint wear.
Hip Pain Radiating to Thigh or Knee
Hip joint problems can cause pain that spreads to nearby areas, such as the thigh, groin, or knee. This happens because nerves and muscles around the hip share pathways with other parts of the leg.
The pain may feel dull, sharp, or burning, depending on the cause. Some people mistake it for a knee problem, delaying proper diagnosis.
Doctors often use physical exams and imaging to trace where the pain originates. Identifying the true source helps determine whether the issue is from the hip joint or another condition.
Inability to Perform Daily Activities
When hip pain and stiffness make it hard to perform everyday tasks, such as dressing, bathing, or driving, it signals serious loss of function.
People may struggle to lift their leg, bend down, or carry objects. This limitation affects independence and can lead to frustration or isolation.

If daily activities become increasingly difficult despite therapy or medication, it may be time to consider further evaluation for possible surgical treatment.
Psychological Impact of Hip Pain
Chronic hip pain affects more than physical health. It can lead to anxiety, irritability, or depression due to constant discomfort and reduced mobility.
People may withdraw from social activities or exercise, which worsens emotional well-being. Sleep problems caused by pain can also heighten stress and fatigue.
Addressing the psychological effects is important. Doctors may recommend counseling, pain management strategies, or support groups to help patients cope while exploring medical options for long-term relief.
Diagnosing the Need for Hip Replacement
Accurate diagnosis ensures that patients receive the right treatment for hip pain and stiffness. Doctors use symptoms, physical exams, and imaging tests to confirm whether hip replacement surgery is necessary or if other conditions such as bursitis or tendonitis are to blame.
Early Signs You Need a Hip Replacement
Common warning signs include persistent hip pain, limited mobility, and stiffness that worsens over time. Many people notice pain in the groin, thigh, or buttock when walking or standing for long periods.
When pain continues despite medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes, doctors may consider hip replacement. According to GoodRx, difficulty standing on one leg or climbing stairs can also signal severe joint damage.
Key indicators:
- Pain that disrupts sleep or daily activity
- Trouble bending or rotating the hip
- Limping or uneven leg movement
- X-ray evidence of bone-on-bone contact
Early recognition helps slow joint deterioration and improves surgical outcomes if replacement becomes necessary.
Hip Arthritis vs. Bursitis vs. Tendonitis
Hip pain can come from different causes. Hip arthritis—especially osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis—involves the gradual breakdown of joint cartilage, leading to stiffness and inflammation. Bursitis, by contrast, affects the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint, causing localized pain on the outer thigh.
Tendonitis occurs when tendons around the hip become irritated, often after overuse or strain. Unlike arthritis, bursitis and tendonitis usually do not cause lasting joint damage.
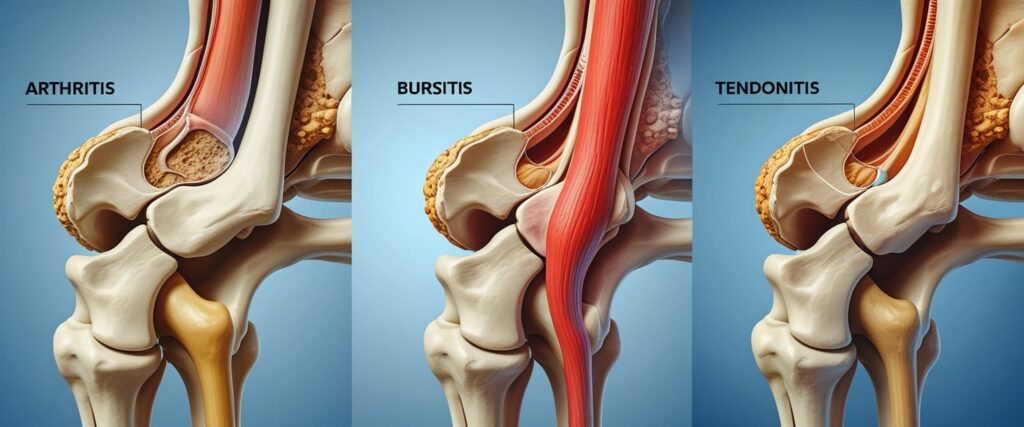
| Condition | Main Cause | Typical Pain Location | Common Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Cartilage wear | Groin, thigh | Anti-inflammatories, surgery if severe |
| Bursitis | Inflamed bursa | Outer hip | Rest, ice, injections |
| Tendonitis | Overuse injury | Front of hip | Stretching, physical therapy |
Identifying the correct condition prevents unnecessary surgery and ensures proper care.
How Doctors Determine if You Need Surgery
Doctors rely on clinical evaluation and imaging to decide if hip replacement is needed. They assess pain intensity, range of motion, and how symptoms affect daily life. If non-surgical treatments fail, surgery becomes an option.
Imaging tests such as X-rays reveal cartilage loss, bone spurs, or narrowed joint space. As explained by Alexander Orthopaedics, severe degeneration visible on scans often confirms the need for surgery. MRI scans may be used to examine soft tissue damage when arthritis or other joint issues are suspected.

Doctors also evaluate how much pain limits walking, sitting, or sleeping. A combination of symptom severity and imaging results guides the final decision.
Where Hip Replacement Pain is Felt
Pain related to hip joint damage often appears in the groin, outer thigh, buttock, or sometimes radiates down the leg. People may mistake it for back pain, but hip pain typically worsens with movement or after sitting for long periods.
According to HealthPartners, early hip arthritis pain may start as mild discomfort and progress to sharp or constant pain. The location of pain depends on which part of the joint is affected.
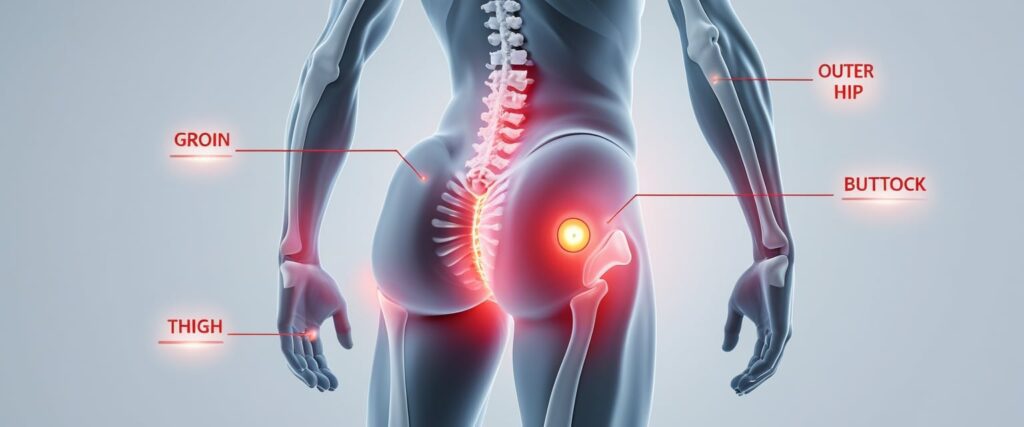
Common pain patterns:
- Groin pain → joint deterioration
- Outer hip pain → bursitis
- Front hip pain → tendonitis
- Buttock pain → referred pain from hip joint
Recognizing the pain’s location helps doctors distinguish between hip arthritis and other soft-tissue conditions, leading to accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Imaging, Tests, and Self-Assessment
Accurate imaging and physical evaluation help doctors confirm whether hip pain comes from arthritis, implant problems, or soft tissue injury. These methods also guide treatment choices and identify early issues before they worsen.
Will an X-Ray Show if I Need a Hip Replacement?
An X-ray is often the first imaging test doctors use to check hip joint damage. It shows bone alignment, cartilage loss, and changes caused by arthritis or implant wear.
Doctors look for narrowed joint space, bone spurs, or implant loosening that may explain pain or stiffness. According to NP Reasoning, imaging is recommended when symptoms persist or worsen despite conservative therapy.
X-rays are fast, low-cost, and widely available. However, they cannot show soft tissue injuries or early cartilage changes. If pain continues despite normal X-rays, additional imaging such as MRI or CT may be needed.
Will an MRI Show if I Need a Hip Replacement?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) provides detailed images of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and cartilage. It helps detect early arthritis, bursitis, or tendonitis that X-rays may miss.
MRI scans are especially useful when doctors suspect hip flexor tendonitis or trochanteric bursitis after replacement surgery. They also help identify infection or inflammation around an implant.
MRI costs vary widely by country. In the United States, a hip MRI can cost between $500–$3,000, while in Türkiye it averages $150–$400, and in India about $100–$300. These differences reflect healthcare pricing, not necessarily image quality.
MRI may not always be necessary if X-rays already show severe joint damage, but it provides valuable insight when symptoms are unclear.
Do I Need a Hip Replacement Quiz
A self-assessment quiz helps people decide if they should consult a specialist. It does not replace medical advice but highlights symptoms worth evaluating.
Typical quiz questions include:
- How often does hip pain interfere with walking or sleep?
- Does pain continue after rest or medication?
- Has mobility or balance decreased over time?
- Is there stiffness or grinding in the joint?
If several answers suggest daily pain or limited movement, a medical exam is recommended. Online tools like the Nuffield Health hip replacement guide can help users reflect on their symptoms before visiting a doctor.
Physical Therapy and Physiotherapy Evaluation
Physical therapy and physiotherapy assessments measure movement, strength, and stability. Therapists check how the hip functions during walking, bending, and standing.
They may use range-of-motion tests and strength measurements to determine if pain comes from joint damage or soft tissue strain. These findings help decide whether surgery or rehabilitation is more appropriate.

Therapists also teach exercises that reduce stiffness and improve balance. As ChiroUp explains, proper hip evaluation helps distinguish hip pain from lumbar or muscular causes.
A structured therapy evaluation ensures that patients receive the right treatment plan, whether surgical or nonsurgical.
Complications and Global Cost Comparison
Complications after hip replacement surgery can include joint dislocation, infection, and soft tissue irritation. Costs for surgery and imaging vary widely by country, with differences in both price and quality of care. Understanding these issues helps patients make informed choices about treatment and recovery.
Dislocated Hip Replacement Symptoms
A dislocated hip replacement occurs when the artificial ball slips out of its socket. This can cause sudden, sharp pain in the hip or groin and make it impossible to move or bear weight. The leg may appear shorter or turned inward or outward.
According to Drugwatch, dislocation or instability accounts for about 15.9% of hip revision surgeries. It often happens soon after surgery or after a fall.
Treatment may include closed reduction, where a doctor repositions the joint without surgery. Repeated dislocations may require revision surgery to adjust or replace the implant. Following movement restrictions and using assistive devices during recovery can reduce the risk of recurrence.
Symptoms of Infection After Hip Replacement
Infection is one of the most serious complications after hip replacement. Early signs include redness, warmth, or swelling around the incision site. Patients may also develop fever, chills, or drainage from the wound.
Deep infections can occur months or even years later and may cause pain, stiffness, and fatigue. As noted by Summit Orthopedics, recognizing these signs early helps prevent severe outcomes.
Treatment depends on the infection’s depth. Superficial infections may respond to antibiotics, while deep infections often require surgical cleaning or implant replacement. Blood tests and imaging help confirm the diagnosis. Maintaining proper hygiene and following post-surgical instructions lower infection risk.
Hip Flexor Tendonitis and Trochanteric Bursitis Symptoms
Hip flexor tendonitis causes pain in the front of the hip or groin, especially when lifting the leg. It can develop from overuse or muscle imbalance after hip replacement surgery. Pain may worsen when climbing stairs or rising from a chair.
Trochanteric bursitis affects the outer hip, where a fluid-filled sac cushions the joint. It leads to tenderness and pain that increases when lying on the affected side. These conditions are not implant failures but soft tissue irritations.
Treatment usually includes rest, stretching, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may help. Proper exercise and posture after surgery reduce the risk of these complications.
Hip Replacement Cost in US, Turkiye, and India
The cost of hip replacement varies by country due to labor, hospital, and implant expenses. Below is an approximate comparison of average total costs for standard hip replacement surgery:
| Country | Average Cost (USD) | Typical Hospital Stay | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $35,000–$60,000 | 3–5 days | Includes surgeon, hospital, and implant fees |
| Turkiye | $7,000–$12,000 | 5–7 days | Popular for medical tourism; modern private hospitals |
| India | $5,000–$9,000 | 5–7 days | Lower cost with skilled orthopedic surgeons |
These figures can change depending on hospital type, implant brand, and patient condition.
Comparing Cost and Quality by Country
The United States offers advanced technology and strict safety standards but at a higher price. Many patients travel to Turkiye or India for lower costs and shorter waiting times.
Turkiye provides internationally accredited hospitals with English-speaking staff and orthopedic specialists trained in Europe or the U.S. India is known for experienced surgeons and affordable care packages that include surgery, medication, and rehabilitation.

Patients should verify hospital accreditation, surgeon credentials, and implant type before deciding. While cost savings are significant abroad, travel and recovery logistics should also be considered.
MRI Cost in US, Turkiye, and India
MRI scans help doctors determine if a hip replacement is needed or if complications exist. Costs differ by region, hospital, and whether contrast dye is used.
| Country | Average MRI Cost (USD) | Typical Wait Time |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $400–$3,500 | 1–7 days |
| Turkiye | $150–$400 | 1–3 days |
| India | $100–$250 | 1–3 days |
MRIs in the U.S. are more expensive due to insurance and facility fees. Turkiye and India offer lower prices with modern imaging equipment.

An MRI can reveal implant loosening, infection, or tissue damage not visible on X-rays. It also helps doctors confirm whether hip pain is due to arthritis, bursitis, or implant failure.
Conclusion
Recognizing the 10 Warning Hip Replacement Symptoms You Must Know: Costs & Global Comparison helps patients take proactive steps toward recovery and improved mobility. Understanding when pain, stiffness, or reduced movement becomes a medical concern can prevent long-term complications and restore comfort faster.
With accurate diagnosis, modern surgical techniques, and affordable global options in Türkiye and India, patients can achieve lasting relief without financial stress. Whether you’re evaluating early warning signs or exploring treatment abroad, knowing these key hip replacement symptoms empowers you to choose the right path to a healthier, more active life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the warning signs that you need a hip replacement?
The key hip replacement symptoms include chronic pain in the groin, thigh, or buttock that worsens with movement, stiffness after rest, and difficulty performing daily activities like climbing stairs or bending. If pain persists despite medication or physical therapy, it’s a clear signal that your hip joint may be severely damaged and a replacement should be considered.
What is the 90% rule with hip replacement?
The 90% rule (also called the hip precaution rule) advises patients not to bend their hip joint beyond a right angle—especially during the first few months after surgery. This means avoiding deep chairs, crossing legs, or bending forward to tie shoes. Following this guideline reduces strain on the artificial joint and lowers the risk of hip dislocation during recovery.
What is the biggest complaint after hip replacement?
After surgery, patients often experience mild stiffness, swelling, or muscle weakness around the hip joint. These issues usually improve with physical therapy and time. Occasionally, people report discomfort when sitting or sleeping on the operated side. Persistent pain could indicate inflammation, soft tissue irritation, or rare complications like bursitis or implant issues.
What conditions are red flags for hip?
Hip red flags include severe and worsening pain, redness or warmth around the joint, fever (possible infection), sudden clicking or locking, and difficulty bearing weight. These symptoms may signal infection, fracture, or dislocation after hip surgery. Immediate medical attention is essential if any of these occur.
What are the symptoms of needing a hip replacement?
Hip replacement symptoms develop gradually and include aching pain in the hip, groin, or thigh, especially when walking or standing for long periods. You may feel stiffness after rest, hear grinding sounds, or notice limited range of motion. When pain interferes with sleep or daily life, it’s time to see an orthopedic specialist.
What pain is associated with hip replacement?
After hip replacement surgery, mild to moderate pain is normal for a few weeks. It may feel like muscle soreness or deep joint aching. Pain typically improves with medication and physiotherapy. If sharp, persistent pain develops months later, it could signal infection, implant loosening, or inflammation and should be evaluated by a doctor.
What are the symptoms of a worn hip joint?
A worn hip joint occurs when cartilage breaks down, causing bones to rub together. Symptoms include deep aching pain, joint stiffness, and a grinding or popping sound (crepitus). The discomfort often worsens after activity or prolonged sitting. Over time, it limits movement and affects posture, often leading to the need for a hip replacement.